Thyroid Cancer: Understanding the Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
- Colin Hurd
- 2 June 2023
- 13 Comments
Unveiling the Mystery: What is Thyroid Cancer?
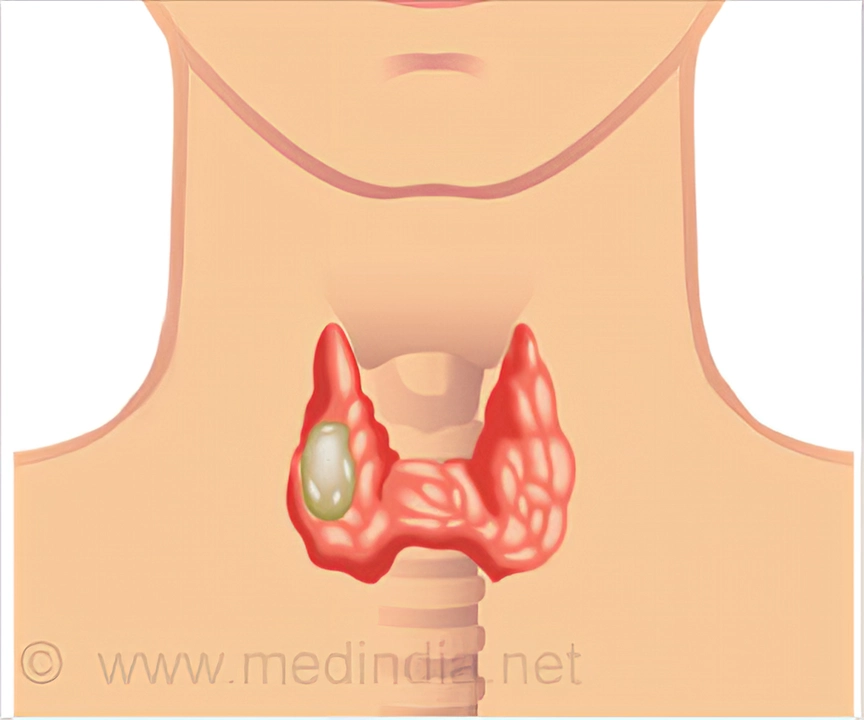
Thyroid cancer is a type of cancer that affects the thyroid gland, which is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located at the base of the neck. The thyroid gland is responsible for producing hormones that regulate our metabolism, growth, and development. When abnormal cells in the thyroid gland grow and multiply uncontrollably, they can form a malignant tumor, leading to thyroid cancer.
There are several types of thyroid cancer, including papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic. Each type has its own unique characteristics and may require different treatment approaches. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for thyroid cancer to help you better understand this disease.
Identifying the Culprits: Causes and Risk Factors of Thyroid Cancer
While the exact cause of thyroid cancer is not yet fully understood, there are certain factors that can increase your risk of developing the disease. Some of these risk factors include:
1. Gender and age: Thyroid cancer is more common in women than in men, and it typically occurs in people between the ages of 30 and 60.
2. Family history: If you have a family history of thyroid cancer or certain genetic conditions, such as familial medullary thyroid cancer or multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN2), you may have an increased risk of developing the disease.
3. Radiation exposure: Exposure to high levels of radiation, particularly during childhood, can increase your risk of developing thyroid cancer later in life.
4. Diet: A diet low in iodine can increase your risk of developing thyroid cancer, particularly in regions where iodine deficiency is common.
It's important to note that having one or more of these risk factors does not necessarily mean you will develop thyroid cancer. However, being aware of them can help you take preventive measures and stay vigilant in monitoring your thyroid health.
Recognizing the Warning Signs: Symptoms of Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid cancer often does not cause any symptoms in its early stages. However, as the cancer grows, you may begin to notice some changes in your body. Some common symptoms of thyroid cancer include:
1. A lump or swelling in the neck: This is often the first sign of thyroid cancer. The lump may be painless and may not cause any other symptoms.
2. Hoarseness or changes in your voice: This can occur if the tumor affects the nerves that control your vocal cords.
3. Difficulty swallowing: A growing tumor may press on your esophagus, making it difficult to swallow food or drink.
4. Difficulty breathing: If the tumor grows large enough, it can compress your trachea (windpipe), causing shortness of breath or wheezing.
5. Pain in the neck or throat: Some people may experience pain in the area of the thyroid gland, particularly when swallowing.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it's important to see your doctor for an evaluation. While they can also be caused by other, less serious conditions, it's always best to rule out thyroid cancer as a possibility.
Diagnosing Thyroid Cancer: Tests and Procedures
If your doctor suspects that you may have thyroid cancer, they will likely perform several tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests may include:
1. Physical examination: Your doctor will examine your neck for any signs of a lump or enlargement in the thyroid gland.
2. Blood tests: Blood tests can help determine if your thyroid is functioning properly and producing the right amount of hormones.
3. Imaging tests: Tests like ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help your doctor visualize the thyroid gland and any abnormalities present.
4. Fine needle aspiration biopsy: During this procedure, your doctor will use a thin needle to remove a small sample of cells from the thyroid gland for examination under a microscope.
The results of these tests will help your doctor determine if you have thyroid cancer, and if so, what type of cancer it is and whether it has spread to other parts of your body.
Battling Thyroid Cancer: Treatment Options
The treatment options for thyroid cancer depend on the type and stage of the cancer, your overall health, and your personal preferences. Some common treatment options include:
1. Surgery: The most common treatment for thyroid cancer is surgery to remove all or part of the thyroid gland. This may be followed by radioactive iodine treatment to destroy any remaining cancer cells.
2. Radioactive iodine treatment: This treatment uses radioactive iodine to target and destroy any remaining thyroid tissue or cancer cells after surgery.
3. External radiation therapy: This treatment uses high-energy X-rays or other types of radiation to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing.
4. Chemotherapy: This treatment uses drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from growing and dividing.
5. Targeted therapy: These drugs specifically target certain characteristics of cancer cells, such as specific proteins or enzymes, to stop their growth.
6. Immunotherapy: This treatment uses your body's own immune system to fight cancer cells.
Your doctor will discuss the most appropriate treatment options for you based on your specific situation and preferences.
Living with Thyroid Cancer: Coping Strategies and Support
Being diagnosed with thyroid cancer can be an overwhelming and emotional experience. It's important to remember that you're not alone, and there are resources available to help you cope with the challenges of living with cancer. Some tips for coping with thyroid cancer include:
1. Educate yourself: Learn as much as you can about your cancer, its treatment, and what to expect during your journey. This can help you feel more in control and better prepared to make decisions about your care.
2. Build a support network: Surround yourself with people who care about you and can offer emotional and practical support, such as friends, family, and support groups.
3. Open communication: Talk openly about your feelings and concerns with your loved ones and healthcare team. They can provide valuable advice, reassurance, and understanding.
4. Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eating well, getting regular exercise, and getting enough sleep can all help improve your physical and emotional well-being during and after treatment.
Don't hesitate to reach out to your healthcare team or local cancer support organizations for additional resources and assistance.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Thyroid Cancer Research and Treatment
Research into the causes, diagnosis, and treatment of thyroid cancer is ongoing, and scientists are continually making advances that can improve the outlook for people with this disease. Some areas of current research include:
1. Improved diagnostic techniques: Developing more accurate and less invasive methods for diagnosing thyroid cancer can help ensure that people receive the most appropriate and effective treatment as early as possible.
2. New treatment options: Researchers are investigating new drugs and therapies that can target specific types of thyroid cancer more effectively, with fewer side effects.
3. Personalized medicine: By better understanding the genetic and molecular characteristics of individual tumors, doctors may be able to tailor treatment plans to each person's unique cancer, improving outcomes and reducing side effects.
As our understanding of thyroid cancer continues to grow, so does our ability to detect, treat, and ultimately, defeat this disease. By staying informed and proactive about your thyroid health, you can play an important role in protecting yourself and supporting the ongoing fight against thyroid cancer.


Comments
dany prayogo
Oh, brilliant, another encyclopedic rundown of thyroid cancer that pretends to uncover secrets no one asked for.
Because obviously the world was lacking a list of causes, symptoms, and treatments that any intern could recite on command.
First, we get the gender and age risk factor, as if a thyroid could read your horoscope and decide to mutate based on your zodiac sign.
Radiation exposure is tossed in like a plot twist in a low-budget sci‑fi movie, yet the article glosses over the fact that modern radiology rarely delivers the megagray doses of the Cold War era.
And of course, iodine deficiency gets a cameo appearance, despite the fact that most Western diets are fortified to the point of absurdity.
The symptom list reads like a vague checklist for any neck complaint, from a sore throat after a bad karaoke night to the occasional hoarseness after shouting at a toddler.
Diagnosing the disease, they say, involves ultrasounds, blood tests, and that fancy fine‑needle aspiration, which sounds more like a culinary recipe than a medical procedure.
Surgery is presented as the hero, followed by radioactive iodine, because nothing says ‘cure’ like ingesting a tiny amount of nuclear material.
External radiation and chemotherapy are mentioned in passing, as if they were optional toppings on a sundae rather than aggressive therapies with significant side effects.
Targeted therapy and immunotherapy get the buzz‑word treatment, yet the article fails to explain the cost or accessibility of these cutting‑edge options.
Living with thyroid cancer, the piece advises, is all about education and support networks, which is fine until you realize most patients are already drowning in medical jargon.
The future research section promises personalized medicine, improved diagnostics, and new drugs, a utopian vision that will probably remain a grant‑writing cliché for years to come.
All in all, the article tries to be a one‑stop shop, but ends up being a laundry list of bullet points that any medical student could copy‑paste.
If you were hoping for a breakthrough revelation, you might want to keep looking elsewhere, perhaps in a peer‑reviewed journal rather than this crowd‑sourced summary.
So, congratulations, dear reader, you are now slightly more informed, and yet still utterly clueless about what to do next.
June 2, 2023 AT 00:42
Wilda Prima Putri
Wow, thanks for the inspiring optimism.
June 7, 2023 AT 22:22
Edd Dan
I think the article does a decent job covering the basics, even if it sometimes feels like a checklist.
It could have delved a bit more into the newer targeted therapies, but overall it's solid.
Also, the risk factor section might overstate the role of diet without enough evidence.
Still, for someone just learning about thyroid cancer, it's a helpful start.
June 13, 2023 AT 20:02
Cierra Nakakura
Totally get what you’re saying! 🙌
Just remember, every patient’s journey is unique, so keep the optimism alive while staying realistic. 😊
We’ve all been there, and sharing info really helps.
June 19, 2023 AT 17:42
Sharif Ahmed
One cannot help but marvel at the sheer grandeur with which the author has woven together the tapestry of thyroid oncology.
The prose, dripping with melodramatic flourish, elevates a mere clinical synopsis to an almost liturgical reverie.
Yet beneath the gilded veneer lies a stark reminder: medicine remains stubbornly tethered to empirical truth, not poetic intrigue.
Thus, while the narrative ascends to lofty heights, the reader must remain grounded in the gritty reality of diagnosis and treatment.
June 25, 2023 AT 15:22
Charlie Crabtree
Great overview! 👍 Keep spreading the word, and remember to stay positive – you’ve got this! 🌟💪
July 1, 2023 AT 13:02
RaeLyn Boothe
I noticed the article never mentioned personal stories or patient experiences, which could make it feel more relatable.
Sharing a bit of real‑life context would really round out the information.
July 7, 2023 AT 10:42
Fatima Sami
While the content is informative, there are several grammatical inconsistencies that detract from its professionalism; for example, the misuse of commas in the symptom section and the lack of parallel structure in the treatment list.
July 13, 2023 AT 08:22
Arjun Santhosh
Thanks for pointing that out – I’ll make sure to tighten up the commas and keep the list parallel.
Your feedback is valuable, and together we can improve the clarity for future readers.
July 19, 2023 AT 06:02
Stephanie Jones
In contemplating the fragile veneer of health, one discerns that cancer is but a reminder of our mortal impermanence.
We chase cures as if they could alter the inexorable march toward entropy.
Yet perhaps the true battle lies not in eradication but in the acceptance of our finite threads.
Such reflections may not ease the physical anguish, but they grant a quiet dignity amidst the storm.
Thus, the article’s clinical tone masks deeper existential queries that remain unaddressed.
July 25, 2023 AT 03:42
Nathan Hamer
Indeed, the intersection of biology and philosophy is a fertile ground for contemplation; however, we must not let abstraction eclipse actionable insight!
Patients need concrete guidance, not just metaphysical musings.
Balancing hope with realism remains the cornerstone of compassionate care.
July 31, 2023 AT 01:22
Tom Smith
Thanks for the thorough summary; just remember, sarcasm aside, the key is early detection and personalized treatment plans.
August 5, 2023 AT 23:02
Kyah Chan
The article exhibits a commendable breadth of coverage; nevertheless, it suffers from a lack of rigorous evidentiary citation and an overreliance on generic statements, which undermines its scholarly merit.
August 11, 2023 AT 20:42