The Impact of Levothyroxine on Menstrual Cycle: What Women Should Know
- Colin Hurd
- 13 May 2023
- 16 Comments
Understanding Levothyroxine and Its Effects on the Body
As women, we often encounter various health concerns that are unique to our gender. One such issue is the impact of certain medications on our menstrual cycle. In this article, we'll be discussing how Levothyroxine, a commonly prescribed medication for thyroid disorders, can affect our periods. But first, let's understand what Levothyroxine is and why it's prescribed.
Levothyroxine is a synthetic form of the hormone thyroxine, which is produced by our thyroid gland. It's prescribed to those suffering from hypothyroidism, a condition where the thyroid gland doesn't produce enough hormones. This can lead to various symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and depression. By taking Levothyroxine, patients can balance their hormone levels and alleviate these symptoms. However, this medication can also have an impact on our menstrual cycles, which is the focus of this article.
How Levothyroxine Can Affect Menstrual Cycles
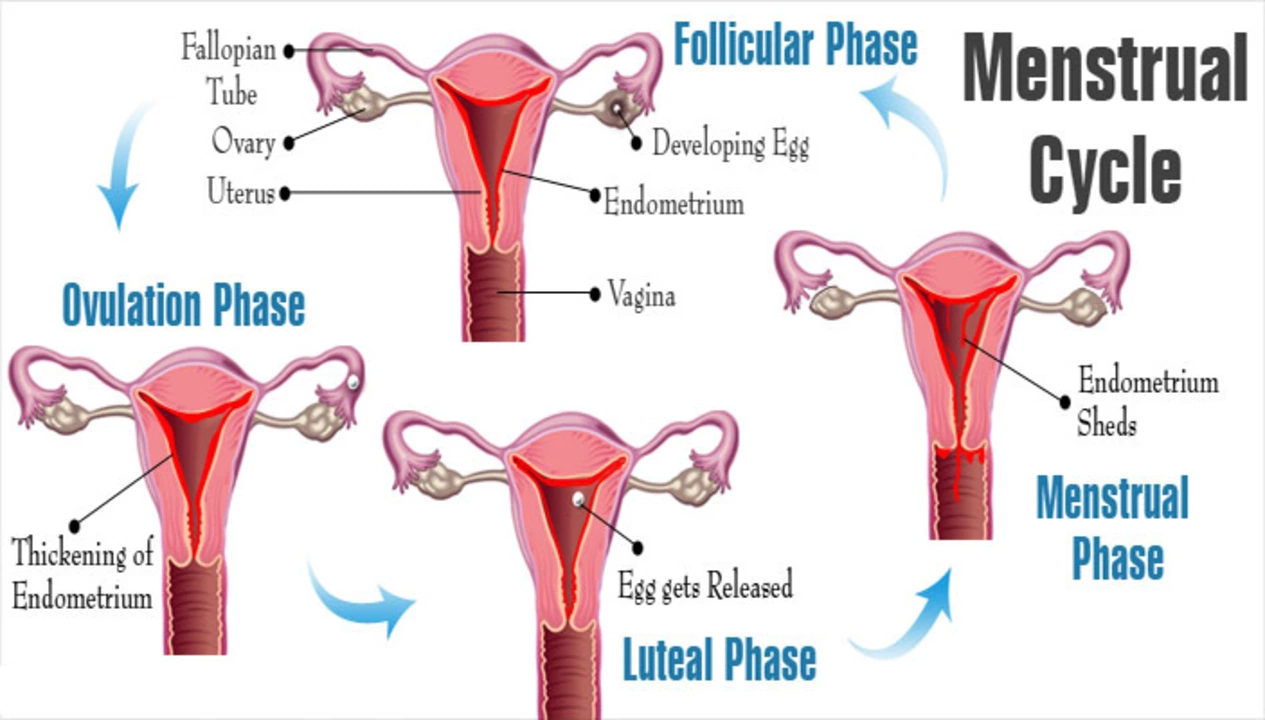
Our menstrual cycles are closely connected to our hormone levels, particularly estrogen and progesterone. When these hormones are imbalanced, it can lead to irregular periods, heavy bleeding, or even missed periods. Levothyroxine, being a hormone replacement medication, can also have an influence on our cycles. So, let's dive into the specifics of how Levothyroxine can impact our periods.
Firstly, it's important to note that not all women taking Levothyroxine will experience changes in their menstrual cycles. Some women might not notice any difference, while others may experience significant changes. The impact largely depends on the individual's body and how it reacts to the medication. That being said, there are a few common ways in which Levothyroxine can affect the menstrual cycle.
1. Irregular Periods
One possible impact of Levothyroxine on the menstrual cycle is causing irregular periods. This can manifest in various ways, such as having periods more frequently, less frequently, or experiencing unpredictable cycles. This happens because the synthetic hormone can interfere with the body's natural hormonal balance, leading to fluctuations in estrogen and progesterone levels.
Irregular periods can be concerning for many women, especially if they're trying to conceive. However, it's essential to remember that these changes are usually temporary and should stabilize once the body gets used to the medication.
2. Heavy or Prolonged Bleeding
Another potential impact of Levothyroxine on the menstrual cycle is heavy or prolonged bleeding during periods. This can occur when the medication affects the balance of estrogen and progesterone, leading to thicker lining in the uterus, which results in heavier bleeding when it sheds. Heavy bleeding can be uncomfortable and cause additional health concerns, such as anemia.
It's crucial to speak with your healthcare provider if you experience heavy or prolonged bleeding while taking Levothyroxine. They may need to adjust your dosage or suggest other treatment options to manage this side effect.
3. Missed Periods
In some cases, Levothyroxine can lead to missed periods or even amenorrhea (absence of menstruation). This can happen if the medication causes a significant imbalance in hormone levels, leading the body to halt the menstrual cycle temporarily. Missed periods can be concerning, especially for those trying to conceive, but it's essential to remember that this side effect is usually temporary.
If you're experiencing missed periods while taking Levothyroxine, it's important to consult with your healthcare provider. They can help determine the cause and suggest possible solutions to restore your menstrual cycle.
Managing the Impact of Levothyroxine on Your Menstrual Cycle
While the potential impact of Levothyroxine on the menstrual cycle can be concerning, it's essential to remember that these side effects are usually temporary and can be managed. Here are some tips on how to manage the impact of Levothyroxine on your menstrual cycle:
1. Work closely with your healthcare provider to monitor your hormone levels and adjust your Levothyroxine dosage if needed.
2. Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, to help support your overall hormonal balance.
3. Keep track of your menstrual cycles, noting any changes or irregularities, to help identify potential issues and discuss them with your healthcare provider.
4. Consider alternative treatments for hypothyroidism if Levothyroxine significantly impacts your menstrual cycle and overall quality of life.
By being proactive in managing the potential side effects of Levothyroxine, you can help ensure a healthy and balanced menstrual cycle.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, it's essential for women taking Levothyroxine to be aware of the potential impact on their menstrual cycles. While not all women will experience changes, it's crucial to monitor your cycles and work closely with your healthcare provider to manage any side effects. Remember, a healthy menstrual cycle is an essential component of overall health and well-being, so don't hesitate to seek help if you're concerned about the impact of Levothyroxine on your periods.




Comments
Sarah Posh
First off, it’s great that you’re paying attention to how Levothyroxine can influence your cycle.
Tracking any changes in period length or flow can give your doctor useful clues.
Sticking to a consistent dosage and checking thyroid labs regularly usually steadies things out.
If you notice heavy bleeding or missed periods, a quick chat with your provider can help fine‑tune the dose.
Remember, you’re not alone; many women navigate this and come out balanced.
May 13, 2023 AT 17:14
James Knight
Wow, another “miracle” drug that supposedly fixes everything – sounds like a marketing ploy to me.
Probably just another excuse for pharma to keep you hooked on pills.
May 13, 2023 AT 22:47
Ajay D.j
I’ve seen a lot of folks in my circle jot down their cycles in a simple spreadsheet, and it surprisingly highlights patterns faster than any lab report.
Even a brief note about energy levels can clue you into how your thyroid meds are settling.
Take it slow, and let the data speak before you jump to conclusions.
May 14, 2023 AT 04:20
Dion Campbell
While your anecdotal spreadsheet may suffice for laypersons, a rigorous endocrinological assessment remains the gold standard, undeniably.
May 14, 2023 AT 09:54
Burl Henderson
Indeed, integrating serum TSH analytics with patient-reported bleed metrics yields a multidimensional model-essential for optimizing Levothyroxine titration protocols.
May 14, 2023 AT 15:27
Leigh Ann Jones
I’ve read through the whole piece and, frankly, it covers the basics without much novelty. Levothyroxine’s role in thyroid hormone replacement is well established, and most clinicians know it. What the article attempts to do is link the drug to menstrual irregularities, which is a real concern for many patients. However, the mechanisms are not fully elucidated, and the text only scratches the surface. One has to consider that hypothyroidism itself can cause heavy or missed periods, independent of medication. Adjusting the dose based on TSH and free T4 values often normalizes the cycle over weeks. Lifestyle factors such as stress, diet, and exercise also weigh heavily on hormonal balance. Some women report that once their thyroid levels are stable, their periods settle down without any further intervention. Conversely, others experience prolonged bleeding that may require an iron supplement or a temporary hormonal bridge. It is essential to communicate any such changes promptly to a healthcare provider, as they may need to tweak the dosage. The article’s suggestion to keep a menstrual diary is sound advice and can empower patients. Nevertheless, a more detailed discussion about potential drug interactions, especially with estrogen-containing contraceptives, would have been beneficial. There is also scant mention of alternative thyroid preparations like liothyronine or natural desiccated thyroid. In practice, a personalized approach, weighing the pros and cons of each option, often yields the best outcomes. Overall, while the guidance is adequate for a general audience, it stops short of providing the depth that a patient navigating these issues might truly need.
May 14, 2023 AT 21:00
Sarah Hoppes
They don’t want you to know the real side effects.
May 15, 2023 AT 02:34
Robert Brown
Stop whining about bleeding, it’s just a hormone tweak.
May 15, 2023 AT 08:07
Erin Smith
Tracking your cycle can really help you see patterns you might miss It’s a simple step that can make a big difference Keep talking to your doctor
May 15, 2023 AT 13:40
George Kent
Honestly, this kind of “just track it” advice is simplistic!!! You need proper medical supervision, not just a diary!!! 🇬🇧🙂
May 15, 2023 AT 19:14
Jonathan Martens
What you’re seeing isn’t a mystery; it’s a classic case of endocrine feedback loops intersecting with the hypothalamic‑pituitary‑gonadal axis.
When the synthetic thyroxine stabilizes metabolic rate, the downstream gonadotropins often readjust, altering endometrial shedding patterns.
That said, individual variability means some patients will notice changes sooner than others.
Keep your records tidy and bring them to the next endocrine consult.
May 16, 2023 AT 00:47
Jessica Davies
While you romanticize feedback loops, the plain truth is that many clinicians overlook the psychosocial burden these fluctuations impose, a fact you conveniently ignore.
May 16, 2023 AT 06:20
Kyle Rhines
It must be noted that the pharmaceutical narrative often downplays adverse events, thereby skewing patient perception.
May 16, 2023 AT 11:54
Jennifer Romand
One cannot help but marvel at the theatrical nature of hormonal upheaval, a drama where Levothyroxine plays both hero and villain.
May 16, 2023 AT 17:27
Kelly kordeiro
In the grand tapestry of endocrine therapeutics, Levothyroxine assumes a role of considerable nuance; its pharmacodynamic profile demands reverent scrutiny.
When administered judiciously, it restores euthyroid homeostasis, yet its influence upon the menstrual milieu can be both subtle and profound.
The oscillation between hyper- and hypothyroidic states, albeit transient, may precipitate endometrial desynchronization, manifesting as irregular bleeding.
Such manifestations, while ostensibly benign, warrant vigilant observation, for they may herald underlying metabolic perturbations.
Moreover, the intersection of exogenous thyroxine with endogenous estrogenic pathways underscores the necessity for interdisciplinary oversight.
Clinicians are thus behooved to integrate gynecologic assessments within the broader therapeutic algorithm.
Patient empowerment through meticulous logging of menstrual parameters further augments clinical acumen.
Consequently, a collaborative, informed approach stands as the quintessential paradigm for navigating these complexities.
May 16, 2023 AT 23:00
Chris Fulmer
It’s clear that Levothyroxine can affect cycles in various ways, but the key takeaway is proactive communication with your healthcare team and diligent self‑monitoring.
By staying informed and sharing observations, you can help tailor treatment to your unique needs and maintain overall well‑being.
May 17, 2023 AT 04:34