Trichomoniasis Symptoms, Causes & Treatment Guide
- Colin Hurd
- 5 October 2025
- 14 Comments
Trichomoniasis Symptom Checker
This symptom checker helps identify potential signs of Trichomoniasis based on gender-specific symptoms. Note that many infections are asymptomatic, so testing is important.
Your symptom analysis will appear here after checking.
When you hear the word Trichomoniasis is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by a single‑celled parasite called Trichomonas vaginalis. It spreads through vaginal or anal sex and can affect anyone who is sexually active, though women typically notice symptoms earlier than men. Understanding the signs, why it happens, and how to clear it up can spare you weeks of discomfort and protect your partner.
What exactly is Trichomoniasis?
Trichomoniasis belongs to the group of protozoan STIs. The parasite lives in the warm, moist environment of the genital tract, where it attaches to the lining and releases enzymes that cause inflammation. In most cases the body’s immune response produces the characteristic discharge and itching, but up to 70% of infected people show no symptoms at all.
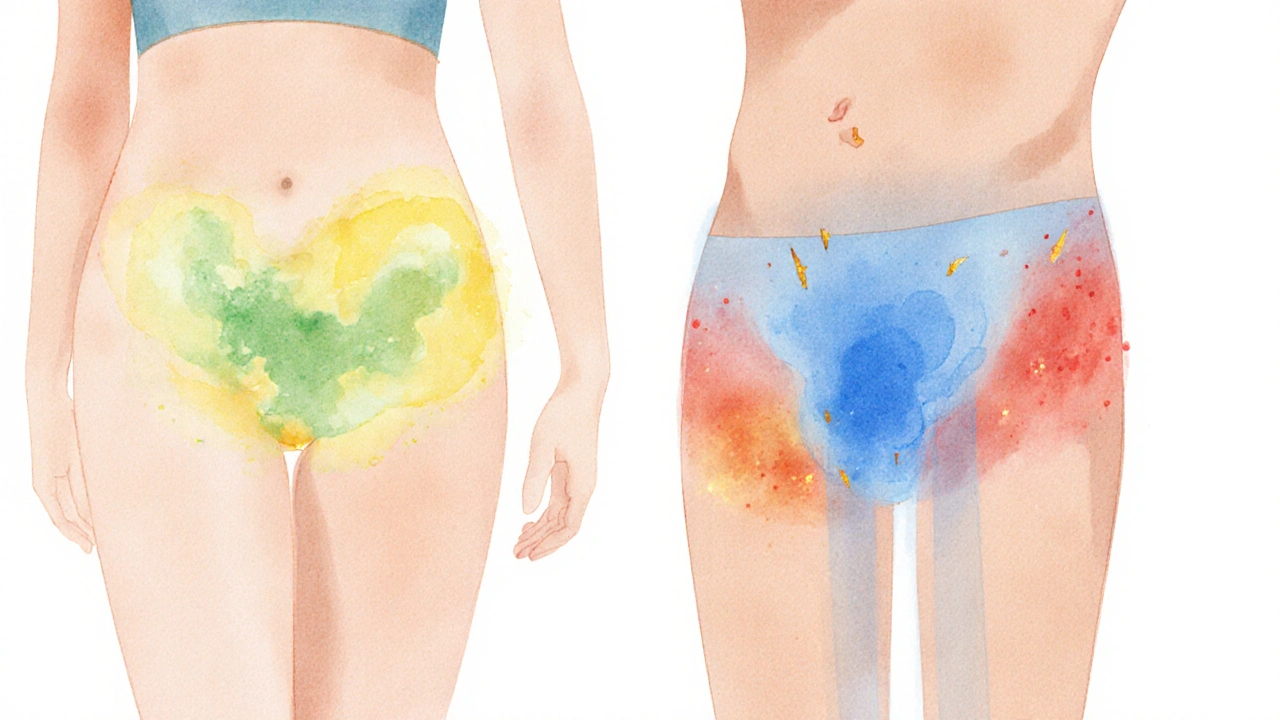
Typical symptoms - what to look for
Symptoms differ by gender, and they can vary from mild irritation to a full‑blown infection.
- Women: frothy, yellow‑green discharge; a strong fishy odor; burning during urination; vaginal itching or soreness; discomfort during intercourse.
- Men: itching or irritation inside the penis; a thin discharge; burning or pain when urinating; sometimes mild discomfort in the urethra.
Because many cases are silent, routine testing is the safest way to know your status.
How does Trichomoniasis spread?
The parasite moves from one partner to another through direct genital contact. Unprotected vaginal or anal sex is the primary route, but sharing sex toys without proper cleaning can also transmit the infection. A single exposure can be enough - even a short encounter with an infected partner puts you at risk.
Diagnosing the infection
Doctors rely on two main methods:
- Microscopic examination of a swab sample, where the parasite’s characteristic shape can be seen under a microscope.
- Rapid antigen tests that detect Trichomonas proteins in minutes. These are increasingly common in clinics because they’re accurate and don’t require a lab.
If you have symptoms, ask your healthcare provider for a test. Even if symptoms have faded, a test is wise after a recent partner change.
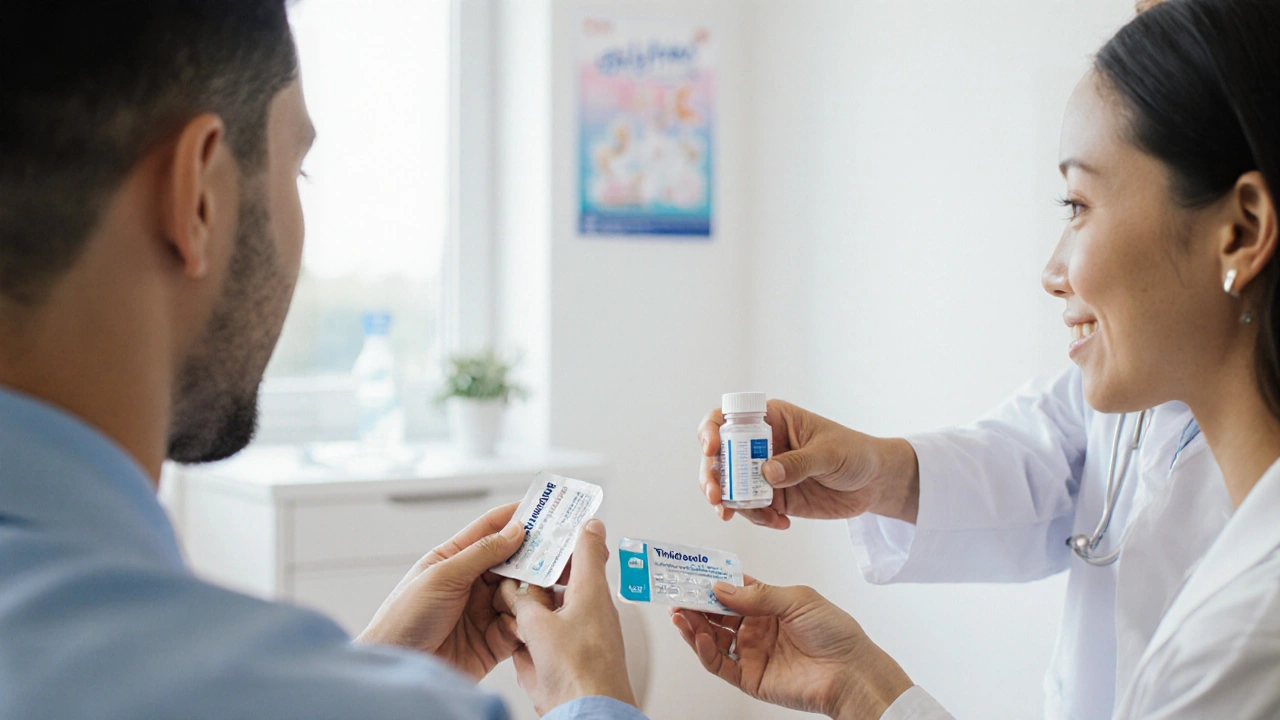
Effective treatment options
Both metronidazole and tinidazole work by killing the parasite. They are taken as a single dose or a short 5‑day course, and cure rates exceed 95% when the full regimen is followed.
| Medication | Typical Dosage | Success Rate | Common Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metronidazole | 2g orally onceor 500mg twice daily for 5days | ≈95% | Nausea, metallic taste, mild headache |
| Tinidazole | 2g orally single dose | ≈96% | Less frequent nausea, occasional dizziness |
Because the infection can hide in the partner’s urethra, it’s essential that both you and any recent sexual partners complete the full course at the same time. A repeat test after two weeks helps confirm that the parasite is gone.
Preventing re‑infection
Here are practical steps to keep Trichomoniasis from coming back:
- Use condoms consistently. Latex barriers stop the parasite from reaching the genital lining.
- Get tested together with any new or recent partner before resuming intimacy.
- Avoid sharing sex toys unless you clean them with hot water and soap or use a fresh condom on each use.
- Limit the number of concurrent sexual partners; fewer partners mean fewer chances for exposure.
Even after treatment, the parasite can linger in the partner’s body for a short time, so a retest for both parties is a smart move.

When to seek medical help
If you notice any of the symptoms listed above, especially a strange discharge or burning during urination, book an appointment with your GP or a sexual health clinic. Pregnant women should be extra careful - untreated trichomoniasis has been linked to pre‑term labor.
Quick reference checklist
- Know the symptoms - discharge, itching, burning.
- Get tested if you have symptoms or a new partner.
- Take the full prescribed dose of metronidazole or tinidazole.
- Ensure your partner completes treatment at the same time.
- Use condoms and clean sex toys to prevent re‑infection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can men be asymptomatic carriers?
Yes. Around 50% of infected men experience no noticeable signs, which is why partner testing is crucial.
Is trichomoniasis a curable infection?
Absolutely. A single course of metronidazole or tinidazole cures more than 95% of cases when taken correctly.
Can I get trichomoniasis from oral sex?
The risk is low but not zero. The parasite prefers moist genital tissue, yet it can survive briefly on the mouth’s lining.
Do I need to abstain from sex after treatment?
It’s best to wait 48hours after finishing medication and until both partners test negative to avoid passing the infection back.
Is trichomoniasis linked to other health problems?
Untreated infection can increase susceptibility to HIV and cause complications during pregnancy, such as low birth weight.


Comments
Patrick McGonigle
Thank you for the thorough guide; it nicely outlines the key steps from recognizing symptoms to confirming a diagnosis. For anyone suspecting an infection, I recommend scheduling a clinic visit promptly, as early testing can prevent complications. The description of microscopy versus rapid antigen tests is particularly useful, and most labs now offer the quicker option. When treatment is prescribed, it is essential to complete the full dosage of metronidazole or tinidazole, even if symptoms improve before the course ends. Adherence not only clears the current infection but also reduces the chance of developing drug‑resistant strains. Moreover, informing recent sexual partners and ensuring they receive treatment simultaneously is crucial to avoid reinfection. Follow‑up testing two weeks after therapy helps confirm eradication, especially for pregnant individuals. Finally, consistent condom use and proper cleaning of shared sex toys remain the most effective preventive measures.
October 5, 2025 AT 13:58
Keisha Moss Buynitzky
It is commendable how the article balances medical detail with practical advice. Readers who are uncertain about their symptoms will appreciate the clear list of discharge characteristics and the emphasis on asymptomatic cases. The recommendation to seek testing even in the absence of noticeable signs reflects a responsible public‑health stance. I also value the reminder that untreated trichomoniasis can have serious implications for pregnancy outcomes. Overall, the piece provides a compassionate roadmap for individuals navigating this condition.
October 16, 2025 AT 08:49
Shivam yadav
Great rundown! I especially like how the guide mentions cultural nuances, like the importance of discussing STI testing with partners in a respectful way. It can be awkward, but the checklist makes the conversation easier. Also, the tip about cleaning sex toys with hot water and soap is something I wish I'd known earlier. Thanks for sharing such a balanced perspective that respects both health and personal values.
October 27, 2025 AT 02:40
pallabi banerjee
This article invites reflection on how we view sexual health in everyday life. The factual tone is anchored by a philosophical reminder: caring for our bodies is an act of self‑respect. By presenting symptoms, diagnostics, and prevention side by side, it encourages readers to act thoughtfully rather than react impulsively. The inclusion of partner treatment underscores the interconnectedness of our choices. A mindful approach, as the guide suggests, can foster both physical well‑being and relational harmony.
November 6, 2025 AT 21:32
Alex EL Shaar
Alright, let’s cut to the chase – this write‑up is as clear as a sunny day in Dublin, but I’ve seen more boring health sheets in a dentist’s waiting room. The "frothy, yellow‑green" description? Nice touch, but why not throw in a meme about fishy odours for good measure? Also, the dosage table could use a splash of colour – maybe neon orange for tinidazole so it pops! And seriously, a sneeze‑like typo "onceor" is adorable, keep it real.
November 17, 2025 AT 16:23
Anna Frerker
Nice facts, but the article could skip the fluff.
November 28, 2025 AT 11:15
Julius Smith
👍 Got the point, short and sweet works best! 😄
December 9, 2025 AT 06:06
Brittaney Phelps
Love the actionable checklist – it makes taking the next step feel doable and less intimidating.
December 20, 2025 AT 00:58
Kim Nguyệt Lệ
The phrase "use condoms consistently" should be "use condoms consistently." Also, avoid the double space before "Latex barriers".
December 30, 2025 AT 19:49
Rhonda Adams
Great vibes! Thanks for breaking down the treatment timeline – it’s reassuring to know the cure rates are so high. Keep spreading the knowledge!
January 10, 2026 AT 14:40
Macy-Lynn Lytsman Piernbaum
Totally agree! 🎉 It’s good to know there’s a solid cure, and the emoji‑friendly tips make it less scary. 😊
January 21, 2026 AT 09:32
Alexandre Baril
The emphasis on partner testing cannot be overstated. When both parties complete treatment simultaneously, the likelihood of recurrence drops dramatically. Additionally, the recommendation for a follow‑up test after two weeks aligns with best practice guidelines and offers peace of mind.
February 1, 2026 AT 04:23
Stephen Davis
First, let’s acknowledge the clear layout of the symptom checker – it provides a user‑friendly interface that anyone can navigate without prior medical knowledge. Second, the article correctly points out that up to 70% of infections can be silent, which underscores the necessity of routine screening. Third, the distinction between microscopy and rapid antigen testing offers readers insight into diagnostic options, allowing them to discuss preferences with their healthcare provider. Fourth, the treatment section highlights both metronidazole and tinidazole, noting dosage variations and success rates that exceed 95 percent when adherence is observed. Fifth, the emphasis on partner treatment is crucial; treating both individuals at the same time prevents the classic ping‑pong effect of reinfection. Sixth, the recommendation for a test‑of‑cure two weeks post‑therapy is a practical step to confirm eradication, especially for pregnant women where complications could be severe. Seventh, preventive measures such as consistent condom use, proper sex‑toy hygiene, and limiting concurrent partners are presented in an accessible checklist format. Eighth, the article’s tone remains factual yet approachable, making it suitable for a wide audience. Ninth, the inclusion of a quick reference checklist at the end serves as a handy reminder for those who may forget details after reading. Tenth, the FAQ section anticipates common concerns, like the possibility of transmission through oral sex and the link to increased HIV susceptibility. Eleventh, the discussion on the infection’s impact during pregnancy highlights the importance of early detection for maternal and fetal health. Twelfth, the resource links and citations, though not exhaustive, provide pathways for further reading. Thirteenth, the design elements, such as hover effects on symptom cards, improve user engagement without overwhelming the content. Fourteenth, the use of plain language alongside medical terminology bridges the gap between laypeople and clinicians. Fifteenth, overall, this guide equips readers with the knowledge to recognize, diagnose, treat, and prevent trichomoniasis, fostering healthier sexual practices and reducing stigma associated with STI discussions.
February 11, 2026 AT 23:15
Grant Wesgate
Nice deep dive, Stephen! 🌟 Staying chill – just remember to double‑check that follow‑up test, and you’ll be good. 😎
February 22, 2026 AT 18:06